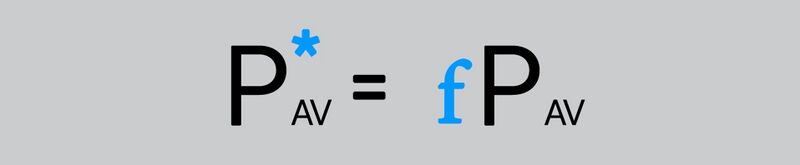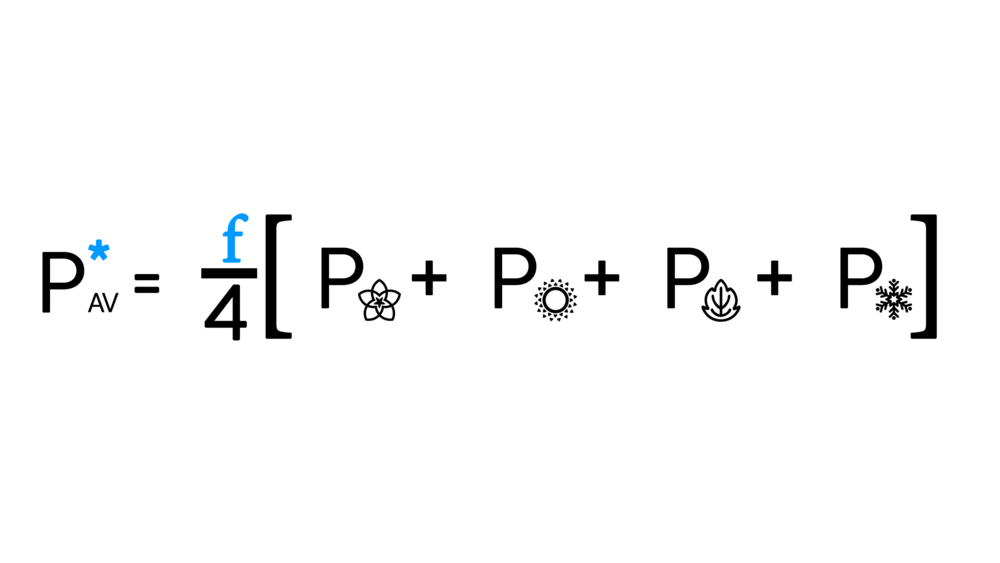Relative Prices: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
Where the average price is given by: | Where the average price is given by: | ||
[[File:Averageprice 4.1.1.png|300px | | [[File:Averageprice 4.1.1.png|300px |right]] | ||
This dimensionless variable is equal to: | This dimensionless variable is equal to: | ||
Revision as of 20:28, 13 June 2023
Proof of Concept. Historical Relative Price Data.
This graph represents the Relative Prices of the four tokens.
On the vertical axis, we have the token’s price divided by the average value of the four token's prices.
Where the average price is given by:
This dimensionless variable is equal to:
- One if the tokens price is equal to the average value.
- It is less than one if the token’s price is lower than the average price.
- And it is bigger than one if the token’s price is above the average price.
This way of presenting the price data is independent of external factors affecting all four tokens' prices. In particular, this chart is independent of the dollar prices of the tokens.
Any change in the price of the tokens due to external factors would affect the numerator and denominator of this fraction in the same proportion. Canceling out its effect on this graph.
This way of presenting the price data concentrates only on changes in the relative value of the tokens. Leaving out the effects of external factors affecting all token prices in the same way.
If all token's prices are affected by the same factor:
Then the new average will be the old average multiplied by the same factor.
Traders profit from oscillations in the relative prices of the four tokens.
And those are independent of the dollar price of the tokens.
==