Brochure: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
Imagine you had four copies of Bitcoin, but their mining supply is not reduced all at once, instead it is arranged in such a way that the bull markets of the four cryptos happen in successive way. When the first crypto reaches an all time high on it's price you could trade it for the crypto whose mining supply will be cut in half next. Then when the second crypto experiences a bull market, you could trade it for the third crypto whose mining supply is going to be reduced next, producing a bull market for the third crypto, and when it reaches an all time high you could trade it for the fourth and so on. | Imagine you had four copies of Bitcoin, but their mining supply is not reduced all at once, instead it is arranged in such a way that the bull markets of the four cryptos happen in successive way. When the first crypto reaches an all time high on it's price you could trade it for the crypto whose mining supply will be cut in half next. Then when the second crypto experiences a bull market, you could trade it for the third crypto whose mining supply is going to be reduced next, producing a bull market for the third crypto, and when it reaches an all time high you could trade it for the fourth and so on. | ||
== | == Solution == | ||
Creating another blockchain comparable to Bitcoin but with a different halving schedule is practically impossible due to the amount of resources needed, both in hardware, energy consumption, and widespread adoption. | Creating another blockchain comparable to Bitcoin but with a different halving schedule is practically impossible due to the amount of resources needed, both in hardware, energy consumption, and widespread adoption. | ||
| Line 113: | Line 113: | ||
== Implemented on Ethereum== | == Implemented on Ethereum== | ||
Token technical data: | |||
| Line 122: | Line 124: | ||
Scheduled halvings cause oscillations in relative price of the tokens. These predictable price oscillations can be used by traders to increase the total number of tokens they have. | Scheduled halvings cause oscillations in relative price of the tokens. These predictable price oscillations can be used by traders to increase the total number of tokens they have. | ||
= Technical Differences with Bitcoin = | [[File:Rate of Production.png |500px |left]] | ||
== Technical Differences with Bitcoin == | |||
* Once the code was deployed it can't be changed. Bitcoin code is mantained by the Bitcoin foundation. | * Once the code was deployed it can't be changed. Bitcoin code is mantained by the Bitcoin foundation. | ||
| Line 143: | Line 148: | ||
* new Opportunities of profit arise from arbitrage | * new Opportunities of profit arise from arbitrage | ||
| Line 150: | Line 154: | ||
* The Relative price chart | * The Relative price chart | ||
[[File:Relative prices.png |800px |right]] | |||
* Halvings | * Halvings | ||
Revision as of 00:35, 6 April 2024
Brochure
BTC halving
Key observation in crypto: BTC halving introduces seasonality
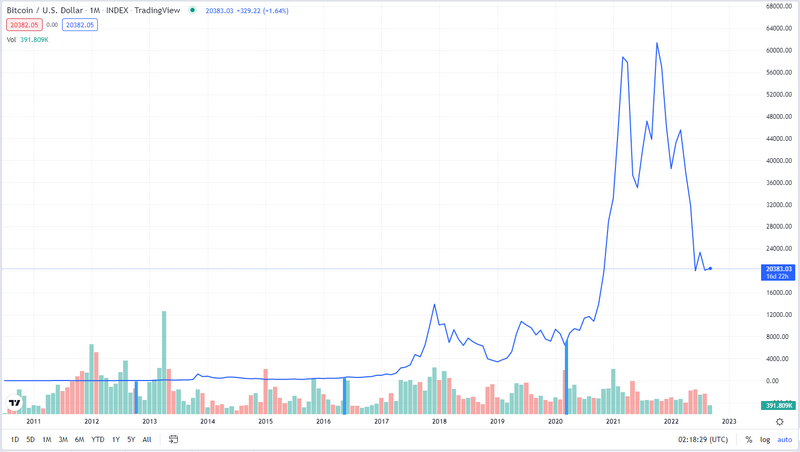
A key observation in cryptocurrency is that the Bitcoin halving of mining supply every 210.000 blocks has introduced a periodic behavior in cryptocurrency markets.
The following chart shows the historical Bitcoin's price. The blue vertical lines mark the dates when the mining supply of bitcoin was cut in half.
(The following info will go in the graph itself --Infographic style)
| date | Reward change in BTC |
|---|---|
| 11/28/2012 | 50 to 25 |
| 07/09/2016 | 25 to 12.5 |
| 05/11/2020 | 12.5 to 6.25 |
| 04/19/2024 | 6.25 to 3.125 |
As you can appreciate, there is nothing particularly enlightening about this graph. It is hard to see the effect of the halving of the mining supply. The price changes are so large that the information is lost in the details of price fluctuations.
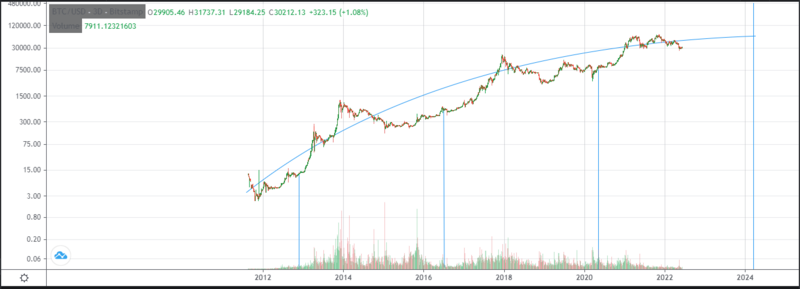
Analysis of the Log(Price) chart. Bull and Bear markets.
If we look at the graph on a logarithmic scale, we can concentrate on the order of magnitude changes, paying less attention to the random fluctuations in the price. Then a pattern emerges:
Every 4 years on average, the mining supply is cut in half. Months after the halving of the mining supply a bull market sends the Bitcoin price to all-time highs, this bull market sends the price way above its cost of production and the whole thing ends up with a price bubble leading to a bear market that may last for years until the next halving occurs.
As the Bitcoin price skyrockets, people starts looking for alternative investments leading to the so called "Altcoin Season", where other major cryptocurrencies experiment a rise in price due to the Bitcoin bull market.
Comment on Bull / Bear markets
The following information will go with the graph:
| date | BTC Price $ | Days after halving to Market Peak | Percent Gain | Days after peak to Market Bottom | Percent Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11/28/2012 | 13 | 335d | 7323% | 638d | 80% |
| 07/09/2016 | 593 | 518d | 2190% | 396d | 76% |
| 05/11/2020 | 9265 | 518d | 557% | 426d | 74% |
| 04/19/2024 | 70000 | ? | ? | ? | ? |
QR with live chart for technical analysis
QR with link to live BTC chart
What Problem is Seasonal Tokens designed to Solve?
In the long term there is no problem. Bitcoin is the best investment of all times. But in the short and mid terms some problems arise.
- For miners: When the halving takes place, the cost of producing Bitcoin doubles overnight. This leaves many miners out of business.
- For Investors: After the bull market reaches it's peak, a bear market follows and typically lasts more than a year. During this time Bitcoin loses about 80% of the value at the peak leaving many investors on a bad situation.
- For Traders: If you have bitcoins, and you want more, you have to gamble. You have to sell the bitcoins when you think the price is going to go down, and then buy more bitcoins after the price has fallen. The price could go up instead of down. You could end up with fewer bitcoins.
The ideal situation would be if there were other cryptocurrencies whose prices are rising while Bitcoin's price is falling.
The problem is that the price of other major cryptocurrencies is highly correlated to Bitcoin's price, and when Bitcoin price falls, it brings all the markets with it.
Imagine you had four copies of Bitcoin, but their mining supply is not reduced all at once, instead it is arranged in such a way that the bull markets of the four cryptos happen in successive way. When the first crypto reaches an all time high on it's price you could trade it for the crypto whose mining supply will be cut in half next. Then when the second crypto experiences a bull market, you could trade it for the third crypto whose mining supply is going to be reduced next, producing a bull market for the third crypto, and when it reaches an all time high you could trade it for the fourth and so on.
Solution
Creating another blockchain comparable to Bitcoin but with a different halving schedule is practically impossible due to the amount of resources needed, both in hardware, energy consumption, and widespread adoption.
But thanks to the Ethereum it is not necessary. The ERC20 technology allows the creation of digital assets with the economic principles embedded in Bitcoin's design. Decentralization and Security are handled by the Ethereum network.
The Seasonal Tokens System
Designed for Investment
- BTC was designed to be money.
- Ethereum is a Decentralized Virtual Computer
- Seasonal Tokens is designed for investment.
The Seasonal Tokens system is an investment instrument to mitigate risk, allowing miners, farmers and traders to participate in the creation of the asset, sharing the risks and profits.
Inspired on Bitcoin
- Issued by Proof of Work.to ensure a fair initial distribution of the assets.
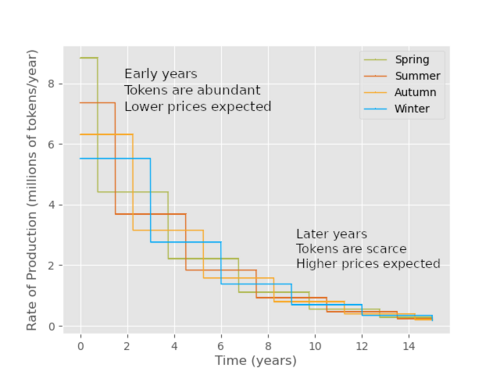
- Decreasing rate of production.Limited supply. About 37 million tokens of each type will be produced in total.
- Halving of mining supply scheduled in time, not in block numbers.
- No governance, once deployed the tokens are only subject to supply and demand.
- No ICO, all investors are on equal footing.
- No Fund rising. All expenses have been paid for. No one is owed anything.
Implemented on Ethereum
Token technical data:
Innovation
The key feature of Seasonal Tokens is that the rates of production have been arranged in time in such a way that every nine months the mining supply of the cheapest token is cut in half.
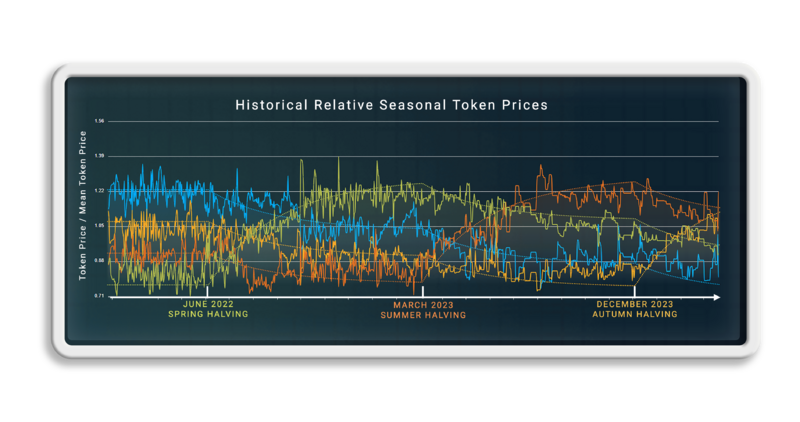
Scheduled halvings cause oscillations in relative price of the tokens. These predictable price oscillations can be used by traders to increase the total number of tokens they have.
Technical Differences with Bitcoin
- Once the code was deployed it can't be changed. Bitcoin code is mantained by the Bitcoin foundation.
- Tokens don't need their own blockchain
What is the Utility?
The utility of Seasonal Tokens is to generate wealth. The ecosystem promotes the interaction of miners, farmers, traders to cooperate in the production of the digital asset, reducing the risks associated.
why don't add more utility?
Water diamond paradox. Ethereum loosing market to other chains. (leads to Polygon section)
Operating on Polygon
- Cost of creation is good for establishing a price
- Operation in ETH is very expensive
- Polygon network solves the problem
- new Opportunities of profit arise from arbitrage
Proof of Concept
- The Relative price chart
- Halvings
- Comments
- QR to proof of concept video