Pitch Deck: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
=The Effects of Changes in Supply Are Visible in the Relative Price Chart= | =The Effects of Changes in Supply Are Visible in the Relative Price Chart= | ||
[[File:HistoricalRelativePriceMay2023.JPG| | [[File:HistoricalRelativePriceMay2023.JPG|800px |left]] | ||
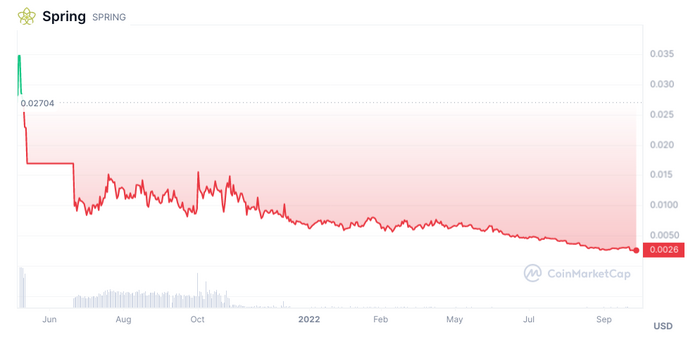
* After the Spring halving in June 2022, Spring went from the cheapest token to the most expensive over the following months. | * After the Spring halving in June 2022, Spring went from the cheapest token to the most expensive over the following months. | ||
| Line 176: | Line 176: | ||
* In the future, it will not be possible to buy 10,000 Autumn tokens every day for any price. | * In the future, it will not be possible to buy 10,000 Autumn tokens every day for any price. | ||
* Autumn will become the most expensive token as the market adjusts to the new scarcity. | * Autumn will become the most expensive token as the market adjusts to the new scarcity. | ||
=Token Statistics= | |||
* About 37 million tokens of each type will be produced in total. | |||
* As of September 2023, the numbers of tokens of each type that exist are: | |||
Spring: 16 million | |||
Summer: 17 million | |||
Autumn: 17 million | |||
Winter: 15 million | |||
* About 20% of the existing tokens are on the market, either on Uniswap on the Polygon or Ethereum chain, or on the centralized exchanges. | |||
* There are about 12,000 Spring tokens, 10,000 Summer tokens, 17,000 Autumn tokens and 15,000 Winter tokens mined every day. | |||
* The current annual inflation rate of the tokens varies between 21% for Summer and 37% for Autumn. | |||
* In about 10 years, the annual inflation rate for each token will be around 1%. | |||
Revision as of 00:02, 3 October 2023
Designed for Investment.
- Bitcoin was designed to be money.
- Ethereum was designed to be a public computer.
- Seasonal Tokens were designed to be an investment.
Similarities with Bitcoin
- Proof-of-work mining
- Decreasing rates of production
- Regular halvings
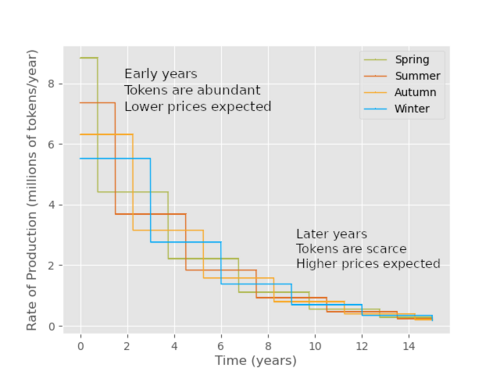
Once every nine months, the rate of production of one of the tokens is cut in half. The token that was produced at the fastest rate becomes the slowest.
In 10 years, the tokens will be produced at about 10% of their current rate. In 20 years, they’ll be produced at about 1% of their current rate.
If demand stays constant (dollars invested per day), the prices will rise as the supply decreases.
Innovation
The changes in the rates of production cause the token prices to cycle around each other.
In June 2022, the rate of production of Spring tokens was halved. Over the following months, Spring went from being the cheapest token to the most expensive. In March 2023, the Summer halving took place. Since then, Summer has gone from the cheapest token to the most expensive.
Trade Tokens for More Tokens
- Investors can trade the more expensive tokens for the cheaper ones, which will become the most expensive later on, allowing the investors to trade again.
- The total number of tokens owned increases with every trade, because the investor always trades tokens for more tokens of a different type.
- This eliminates the risk of making a loss measured in tokens.
- The risk of making a loss measured in dollars cannot be eliminated.
- An investor who turns 10 Spring tokens into 30 Spring tokens by trading will have more wealth than an investor who simply holds the 10 Spring tokens.
- “Trade tokens for more tokens” outperforms the buy-and-hold strategy.
Example
- An investor who started with 10 Winter tokens before June 2022 could have traded them for about 15 Spring tokens.
- Those 15 Spring tokens could have been traded for about 21 Summer tokens before March 2023.
- 21 Summer tokens can be traded for about 27 Autumn tokens today.
- It is expected that, before September 2024, it will be possible to trade 27 Autumn tokens for about 35 Winter tokens.
- By turning 10 Winter tokens into 35 Winter tokens, an investor can make a profit without relying on an increase in the dollar prices of the tokens.
The Main Difference Between Seasonal Tokens and Bitcoin
- If you have bitcoins, and you want more, you have to gamble.
- You have to sell the bitcoins when you think the price is going to go down, and then buy more bitcoins after the price has fallen.
- The price could go up instead of down. You could end up with fewer bitcoins.
- Investors who hold Seasonal Tokens can gain more tokens over time without gambling.
- They don’t need to speculate about the future when they trade tokens for more tokens. They don’t risk ending up with fewer tokens.
More Similarities Between Bitcoin and Seasonal Tokens
- There is no Seasonal Tokens corporation.
- The founders of the project need to buy and mine the tokens to acquire them, like everyone else.
- There was no ICO and no fundraising. The costs of developing the project have been fully covered by the founders. No one is owed anything.
- Nobody is in control of the tokens. There is no governance.
- Every investor is on an equal footing.
Differences Between Bitcoin and Seasonal Tokens
- Bitcoin has its own blockchain, peer-to-peer network, wallet software and block explorers.
- Seasonal Tokens run on the Ethereum blockchain as smart contracts, and they do not need any supporting infrastructure or software.
- As ERC-20 tokens, Seasonal Tokens can be stored in existing wallet software, mined using existing mining software, and traded on decentralized exchanges.
- Bitcoin’s software can be upgraded.
- The Seasonal Tokens smart contracts are set in stone and will continue to run in their current form for as long as Ethereum exists.
- Bitcoin needs massive mining power to secure the blockchain.
- Seasonal Tokens can survive indefinitely with only a single miner using a single GPU.
What Can the Tokens be Used For?
- The primary intended use of the tokens is to trade them for more tokens.
- Trading tokens for more tokens over time helps the miners to mine more efficiently, because it helps to keep the market prices aligned with the cost of production.
- Investors who gain tokens over time by trading earn the tokens they acquire, by providing this valuable service to miners.
- In practice, the tokens are used for many purposes, including tipping, farming, and arbitrage.
- Large discrepancies between token prices allow investors to trade tokens for more tokens at a favorable rate.
- The tokens allow investors to convert volatility into profit, while keeping the market prices rational. When a large fluctuation appears, investors get an opportunity to trade tokens for a lot more tokens.
Why Not Add More Utility?
- The tokens are designed for investment. Their decreasing rates of production make them suitable for use as a long-term store of value.
- Adding utility would exert downward pressure on the long-term prices of the tokens because of the Diamond-Water Paradox:
* Adam Smith, in The Wealth of Nations, explained that there are two types of value: value for use and value for exchange. * The things that have the highest value for use tend to have the lowest value for exchange. Water is useful but can’t be exchanged for much. * The things that have the highest value for exchange tend to have little or no use, e.g. diamonds.
- The explanation of the paradox is that it benefits society when useful things are cheap, so society builds infrastructure to make useful things as cheap as possible. Oil would be much more expensive if it was useless.
- It harms no one when diamonds are expensive, because nobody needs a diamond.
- It will harm no one if Seasonal Tokens become very expensive.
The Diamond-Water Paradox Applies to Cryptocurrencies Too
- Ethereum is very useful. People need it to interact with smart contracts. People should be able to get Ethereum for free, like safe drinking water.
- Bitcoins are not useful. Nobody needs a bitcoin. Society will not try to make bitcoins more affordable.
- After Ethereum became expensive to use, it lost 25% of its market share to competing smart-contract blockchains.
- Bitcoin has lost 2% of its market share to competing proof-of-work coins.
- There is no demand for Bitcoin’s utility at a lower price, because there is no utility.
- Ethereum’s utility is exerting downward long-term pressure on its price. Bitcoin’s lack of utility is allowing it to remain expensive.
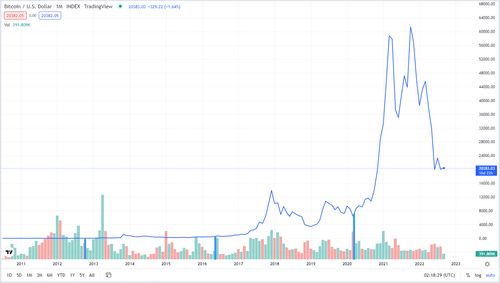
Supply and Demand Are Visible in Different Price Charts
- The demand for the tokens is visible in the USD price charts.
- The effect of the cut in supply is not visible in the USD price charts.
- Demand for the tokens has fallen along with the broader crypto market.
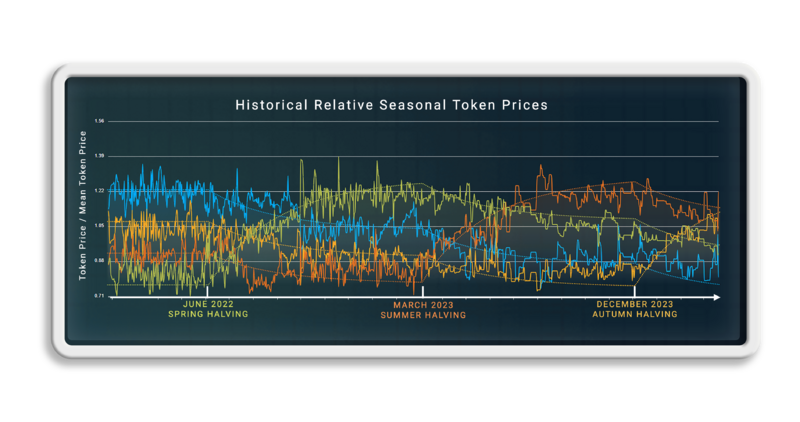
The Effects of Changes in Supply Are Visible in the Relative Price Chart
- After the Spring halving in June 2022, Spring went from the cheapest token to the most expensive over the following months.
- This is clearly visible in charts when the prices are expressed in terms of the average price of the four tokens.
- The effects of demand for the tokens are not visible in this chart.
- The Winter/Spring exchange rate does not depend on external factors such as the popularity of the project.
Low Prices Are Not Bad
- The Seasonal Tokens internal economy is highly robust, and can survive in conditions of extremely low prices.
- A single miner with a single device, and a single investor spending a few cents a day, could keep the prices cycling around each other indefinitely.
- The tokens and their internal economy are highly survivable. Low prices do not threaten the survival of the tokens.
- There is no business that can go bankrupt.
- Miners are making a profit, although low prices mean fewer miners.
- Regular buyers are very happy with the low prices.
Low Prices Today Can Lift People Out of Poverty in the Future
- On Discord, there is a Seasonal Tokens Investors Club server.
- Members of the server have access to a bot that makes regular token purchases and sends tokens to club members.
- Some of the club members are living in poor countries and spend a few cents a day on tokens.
- Today’s market prices don’t reflect the future scarcity of the tokens, but talented individuals in poor countries can understand the future scarcity.
- If Seasonal Tokens can lift people out of poverty over the long term, then it can be a force for genuine good in the world.
- There is no immediate rush to make the prices of the tokens go to the moon.
Regular Buying is the Only Rational Way to Invest
- There are currently more than 10,000 tokens of each type produced every day by miners.
- For the price of the tokens to reach $1 today, more than $40,000 would need to be spent buying tokens every day.
- The prices will remain low while the tokens are being produced this quickly.
- Holders are not happy with low prices. They don’t benefit from the low prices. They are impatient. They want the price to go to the moon tomorrow.
- Regular buyers are happy with low prices. When prices are low, regular buyers benefit.
- While the tokens are being produced quickly, it is better to be a regular buyer than a holder.
The Effects of The Autumn Halving In December 2023
- On the 5th of December, 2023, the rate of production of Autumn tokens will be cut in half.
- There are 120 Autumn tokens mined every 10 minutes today. Next year, there will be 60.
- In September 2023, it’s possible to buy 10,000 Autumn tokens every day for a fraction of a cent each.
- In the future, it will not be possible to buy 10,000 Autumn tokens every day for any price.
- Autumn will become the most expensive token as the market adjusts to the new scarcity.
Token Statistics
- About 37 million tokens of each type will be produced in total.
- As of September 2023, the numbers of tokens of each type that exist are:
Spring: 16 million Summer: 17 million Autumn: 17 million Winter: 15 million
- About 20% of the existing tokens are on the market, either on Uniswap on the Polygon or Ethereum chain, or on the centralized exchanges.
- There are about 12,000 Spring tokens, 10,000 Summer tokens, 17,000 Autumn tokens and 15,000 Winter tokens mined every day.
- The current annual inflation rate of the tokens varies between 21% for Summer and 37% for Autumn.
- In about 10 years, the annual inflation rate for each token will be around 1%.